QuickLogic EOS™ S3 MCU + eFPGA SoCs
QuickLogic EOS™ S3 MCU + eFPGA SoCs are multi-core, ultra-low power sensor-processing Systems-on-a-Chip designed for mobile market applications such as smartphones, wearables, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. The core of the EOS S3 SoC platform is the proprietary µDSP-like Flexible Fusion Engine (FFE). To complement the FFE, the EOS S3 SoCs also include an Arm® Cortex®-M4 subsystem that enables higher level, general-purpose processing. This multi-core approach, along with multiple power islands, allows the EOS S3 SoCs to process sensor data and run algorithms in the most processing and power-efficient manner possible.The QuickLogic EOS S3 MCU + eFPGA SoCs are offered in WLCSP42 and BGA64 packages with a -20°C to +85°C operating temperature range.
Features
- Multi-Core Design
- Ultra-low power μDSP-like Flexible Fusion Engine (FFE) for always-on, real-time sensor fusion algorithms, an Arm Cortex M4-F floating-point processor for general purpose processing, and on-chip programmable logic for flexibility and integration of additional logic functions to a single device
- Multiple, concurrent cores enable algorithm partitioning capability to achieve the most power and computationally efficient sensor processing system-on-a-chip (SoC) in the market
- Cortex-M4-F Processor
- Up to 80MHz operating speed
- Up to 512KB SRAM with multiple power modes, including deep sleep
- Ideal for computationally intensive sensor processing algorithms (continuous heart rate monitor, indoor navigation, always-on voice triggering, etc.)
- Third-Generation Flexible Fusion Engine (FFE)
- Up to 10MHz operating frequency
- 50KB control memory
- 16KB data memory
- μDSP-like architecture for efficient mathematical computations
- Ideal for always-on, real-time sensor fusion algorithms (such as pedometer, activity classification, gesture recognition, and others)
- Communication Manager
- Communicates with host applications processor through its SPI Slave
- Up to 20MHz
- Audio support for Pulse Density Modulation (PDM) or I2S microphones
- Optional hardware PDM bypass path to forward microphone data to application processor or Voice CODEC
- Dedicated logic for PDM to Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) conversion
- Dedicated hard logic integration of Sensory Low Power Sound Detect (LPSD) for on-chip voice recognition
- Sensor Manager
- 5KB x 18-bit memory
- Completely autonomous (zero load on the M4-F) initialization and sampling of sensors through hard-wire I2C or configurable I2C/SPI
- Programmable Fabric (FPGA)
- 2400 effective logic cells with 64Kbit RAM available
- Eight RAM FIFO controllers
- Provides the capability to add logic functions or augment existing logic functions
- Additional Features
- On-device circuit to support 32.768kHz clock or crystal oscillator
- Dual Low-Dropout (LDO) regulators for on-chip regulation
- Power Management Unit (PMU) for minimizing power in all conditions (idle, deep sleep, and shut down)
- SPI Master, SPI Slave, I2S Master, I2S Slave, and I2C interfaces
- Audio support for PDM or I2S microphones
- Internal codec available for Pulse Density Modulation (PDM) to Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) conversion
- 12-bit ΔΣ Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) for battery monitoring
- 2-pin Serial Wire Debug (SWD) port
- System DMA engine for efficient data movement
- eFuse memory for storing AES Key, voltage trim, and other configurable information
- Operating System Support
- Android OS
- Real-Time Operating System (RTOS) compatible
- Package Options
- 2.66mm x 2.42mm x 0.51mm 42-ball WLCSP (27 user I/O, 2 VCCIO banks)
- 3.5mm x 3.5mm x 0.71mm 64-ball BGA (46 user I/O, 2 VCCIO banks)
Applications
- Smartphones
- Wearables
- Always-on voice applications
- AI inferencing at the edge/endpoint
- General-purpose Internet of Things (IoT) applications
Products by Category
- EOS S3 Ultra Low Power Sensor/Voice Processor + eFPGA
- EOS S3 Ultra Low Power Sensor/Voice Processor + eFPGA (Low Voltage)
- EOS S3 Ultra Low Power MCU + eFPGA EOS S3 Ultra Low Power MCU + eFPGA (Low Voltage)
Videos
Block Diagram
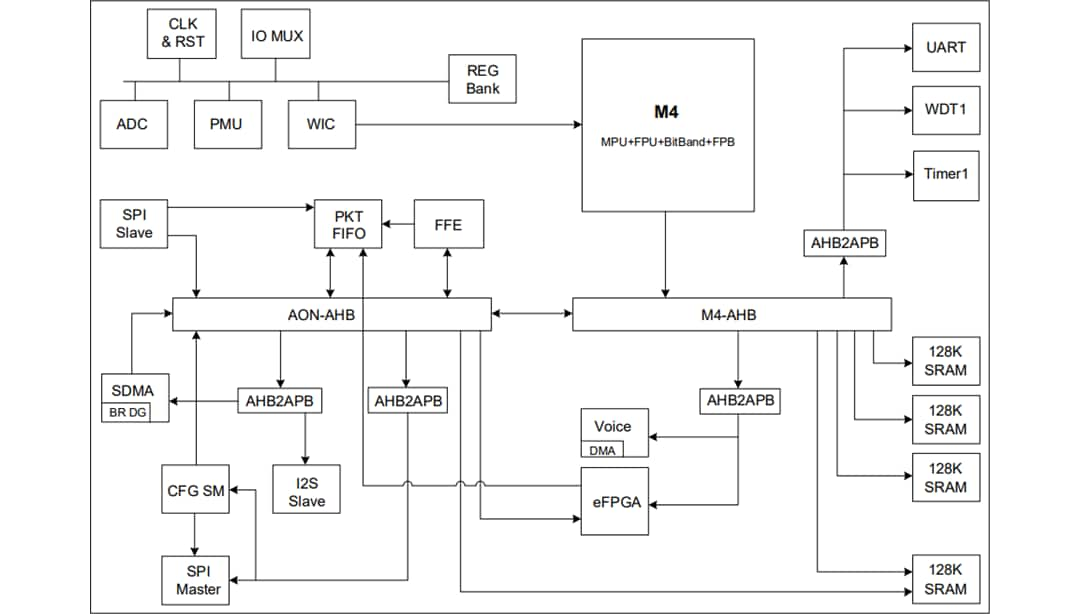
Simplified Platform Architecture

Opublikowano: 2021-03-08
| Zaktualizowano: 2022-03-11